Best Esophagus Surgeon In Ahmedabad
- Hiatus Hernia surgery
- GERD surgery
- Surgery for Esophagus obstruction / Strictures
- Surgery for Esophageal Cancer
- Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR)
- Endoscopic Submucosal Dissetion (ESD)
- Upper GI Endoscopy
- Banding and Glue for Variceal Bleeding
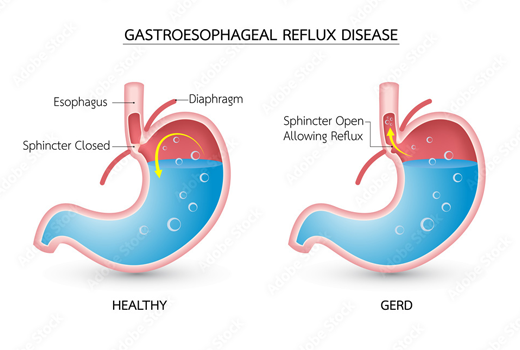
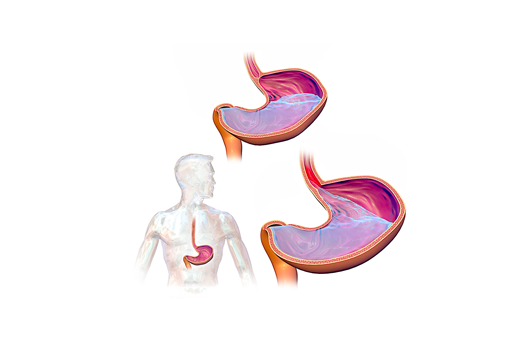
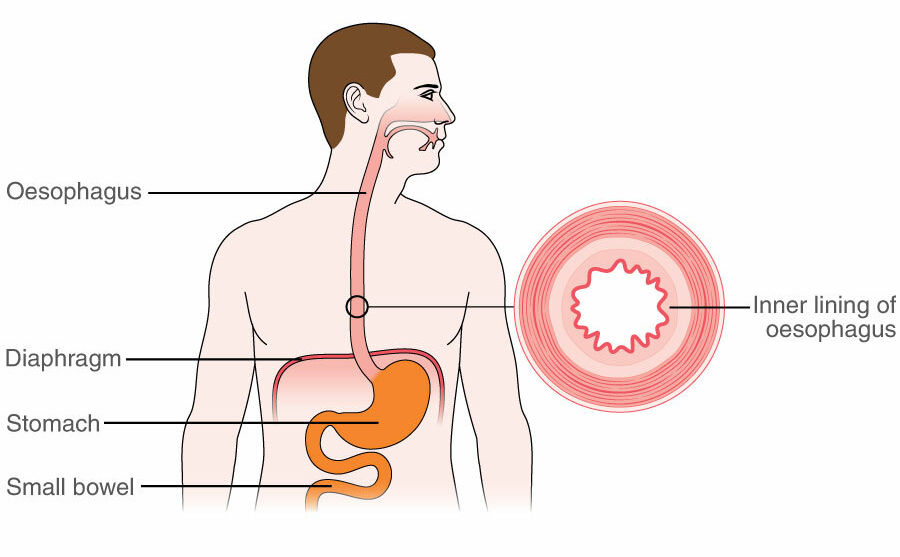
What is Esophagus ?
The esophagus, a muscular tube connecting the throat to the stomach, is vital for proper digestion and plays a crucial role in maintaining overall digestive health.
Common Problems Encountered
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) : Chronic acid reflux causing irritation.
- Barrett's Esophagus : Changes in esophageal lining due to prolonged GERD.
- Esophageal Stricture : Narrowing causes swallowing difficulties.
- Achalasia : Impaired esophageal motility hindering food passage.
- Esophageal Cancer : Malignant growth requires specialized attention.
Common Symptoms
- Persistent heartburn
- Difficulty or pain while swallowing
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Regurgitation of food or sour liquid
- Chronic cough or hoarseness
- Unexplained weight loss
Common Causes
- Chronic acid reflux (GERD)
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Genetic predisposition
- Barrett's esophagus
- Certain medications